Skop Lab Publications
- Skop, A., Schindler, K. Localized translation in the embryo. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2024). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-024-00725-z
- Patel, S., Park, S., Torr, E., Zhu, D., Dureke, AG, McIntyre, A., Muzyka, N., Severson, J., Skop, AR. (2024) The biogenesis of large extracellular vesicles occurs during mitosis. In revision.
- Patel, S, Park S., Torr, E., Dureke, AG, McIntyre, A, Skop, AR. (2023). A protocol for the isolation of large extracellular vesicles or midbody remnants from human cell culture medium using 1.5% PEG 6000 and gold nanoparticles and MKLP1 as a marker. CellSTAR protocols, Volume 4, Issue 4, 15 December 2023, 102562 doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xpro.2023.10256
- Jung, GI, Londono-Vasquez, D., Park, S., Skop, AR., Balboula, A., Schindler, K. (2023). A meiotic midbody structure in mouse oocytes acts as a barrier for nascent translation to ensure developmental competence. Nature Communications, In revision. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.17.516899
- Park, S., Dahn, RD, Kurt, E., Presle, A, VanDenHeuvel, K., Moravec, C., Jambhekar, A., Olukoga, O., Shepherd, J., Echard, A., Blower, MD., Skop, AR (2023). The midbody and midbody remnant are assembly sites for RNA and active translation. Developmental Cell, Aug 1:S1534-5807(23)00357-X. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.07.009. Online ahead of print. PMID: 37552987
- Del Castillo U, Gnazzo MM, Sorensen Turpin CG, Nguyen KCQ, Semaya E, Lam Y, de Cruz MA, Bembenek JN, Hall DH, Riggs B, Gelfand VI, Skop AR. Conserved role for Ataxin-2 in mediating endoplasmic reticulum dynamics. Traffic. 2019,Jun;20(6):436-447. doi: 10.1111/tra.12647. Epub 2019 May 8. PubMed PMID:30989774; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6553494.
- Billmyre KK, Doebley AL, Spichal M, Heestand B, Belicard T, Sato-Carlton A,Flibotte S, Simon M, Gnazzo M, Skop A, Moerman D, Carlton PM, Sarkies P, Ahmed S.The meiotic phosphatase GSP-2/PP1 promotes germline immortality and small RNA-mediated genome silencing. PLoS Genet. 2019 Mar 28;15(3):e1008004. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008004. eCollection 2019 Mar. PubMed PMID: 30921322; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6456222.
- Skop AR. The entrance: how life experience shaped my passion for diversity and inclusion. Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Nov 1;29(22):2608-2610. doi:10.1091/mbc.E18-07-0431. PubMed PMID: 30376436; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6249843.
- Bonner MK, Han BH, Skop AR. Correction: Profiling of the Mammalian Mitotic Spindle Proteome Reveals an ER Protein, OSTD-1, as Being Necessary for Cell Division and ER Morphology. PLoS One. 2017 Jan 30;12(1):e0171399. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171399. eCollection 2017. PubMed PMID: 28135330; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5279803.
- Gnazzo MM, Uhlemann EE, Villarreal AR, Shirayama M, Dominguez EG, Skop AR. The RNA-binding protein ATX-2 regulates cytokinesis through PAR-5 and ZEN-4. Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 15;27(20):3052-3064. Epub 2016 Aug 24. PubMed PMID: 27559134;PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5063614.
- Gnazzo MM, Skop AR. Spindlegate: the biological consequences of disrupting traffic. Dev Cell. 2014 Mar 10;28(5):480-2. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2014.02.014. PubMed PMID: 24636255.
- Bonner MK, Han BH, Skop A. Profiling of the mammalian mitotic spindle proteome reveals an ER protein, OSTD-1, as being necessary for cell division and ER morphology. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 10;8(10):e77051. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077051. eCollection 2013. Erratum in: PLoS One. 2017 Jan 30;12 (1):e0171399. PubMed PMID: 24130834; PubMed Central PMCID:PMC3794981.
- Pittman KJ, Skop AR. Anterior PAR proteins function during cytokinesis and maintain DYN-1 at the cleavage furrow in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012 Oct;69(10):826-39. doi: 10.1002/cm.21053. Epub 2012 Aug 10. PubMed PMID: 22887994; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3650724.
- Shivas JM, Skop AR. Arp2/3 mediates early endosome dynamics necessary for the maintenance of PAR asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell. 2012 May;23(10):1917-27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0006. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PubMed PMID: 22456506; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3350555.
- Ai E, Poole DS, Skop AR. Long astral microtubules and RACK-1 stabilize polarity domains during maintenance phase in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. PLoS One. 2011 Apr 20;6(4):e19020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019020. PubMed PMID:21533050; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3080402.
- Bonner MK, Poole DS, Xu T, Sarkeshik A, Yates JR 3rd, Skop AR. Mitotic spindle proteomics in Chinese hamster ovary cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20489.doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020489. Epub 2011 May 27. PubMed PMID: 21647379;PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3103581.
- Shivas JM, Morrison HA, Bilder D, Skop AR. Polarity and endocytosis:reciprocal regulation. Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;20(8):445-52. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 May 20. Review. PubMed PMID: 20493706;PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2917511.
- Ai E, Skop AR. Endosomal recycling regulation during cytokinesis. Commun Integr Biol. 2009 Sep;2(5):444-7. PubMed PMID: 19907714; PubMed Central PMCID:PMC2775247.
- Nakayama Y, Shivas JM, Poole DS, Squirrell JM, Kulkoski JM, Schleede JB, Skop AR. Dynamin participates in the maintenance of anterior polarity in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo. Dev Cell. 2009 Jun;16(6):889-900. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2009.04.009. PubMed PMID: 19531359; PubMed Central PMCID:PMC2719978.
- Ai E, Poole DS, Skop AR. RACK-1 directs dynactin-dependent RAB-11 endosomal recycling during mitosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Mar;20(6):1629-38. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-09-0917. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Erratum in:Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Dec;20(23):5036. PubMed PMID: 19158384; PubMed Central PMCID:PMC2655251.
- Bonner MK, Skop AR. Cell division screens and dynamin. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Jun;36(Pt 3):431-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0360431. Review. PubMed PMID: 18481974; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3660067.
- Zhang H, Skop AR, White JG. Src and Wnt signaling regulate dynactin accumulation to the P2-EMS cell border in C. elegans embryos. J Cell Sci. 2008, Jan 15;121(Pt 2):155-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.015966. PubMed PMID: 18187449.
- Dinkelmann MV, Zhang H, Skop AR, White JG. SPD-3 is required for spindle alignment in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos and localizes to mitochondria. Genetics. 2007 Nov;177(3):1609-20. Epub 2007 Oct 18. PubMed PMID: 17947426;PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2147968.
- Konopka CA, Schleede JB, Skop AR, Bednarek SY. Dynamin and cytokinesis.Traffic. 2006 Mar;7(3):239-47. Review. PubMed PMID: 16497219; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3654675.
- Otegui MS, Verbrugghe KJ, Skop AR. Midbodies and phragmoplasts: analogous structures involved in cytokinesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;15(8):404-13.Review. Erratum in: Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;15(10):517. PubMed PMID: 16009554;PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3677513.
- Skop AR, Liu H, Yates J 3rd, Meyer BJ, Heald R. Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science. 2004 Jul 2;305(5680):61-6. Epub 2004 May 27. PubMed PMID: 15166316; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3679889.
- Thompson HM, Skop AR, Euteneuer U, Meyer BJ, McNiven MA. The large GTPase dynamin associates with the spindle midzone and is required for cytokinesis. Curr Biol. 2002 Dec 23;12(24):2111-7. PubMed PMID: 12498685; PubMed Central PMCID:PMC3690653.
- Skop AR, Bergmann D, Mohler WA, White JG. Completion of cytokinesis in C.elegans requires a brefeldin A-sensitive membrane accumulation at the cleavage furrow apex. Curr Biol. 2001 May 15;11(10):735-46. PubMed PMID: 11378383; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3733387.
- Skop AR, White JG. The dynactin complex is required for cleavage plane specification in early Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Curr Biol. 1998 Oct8;8(20):1110-6. PubMed PMID: 9778526; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3690630.
In the news
"One Man's Trash...", The Scientist, Dec 1st, 2013
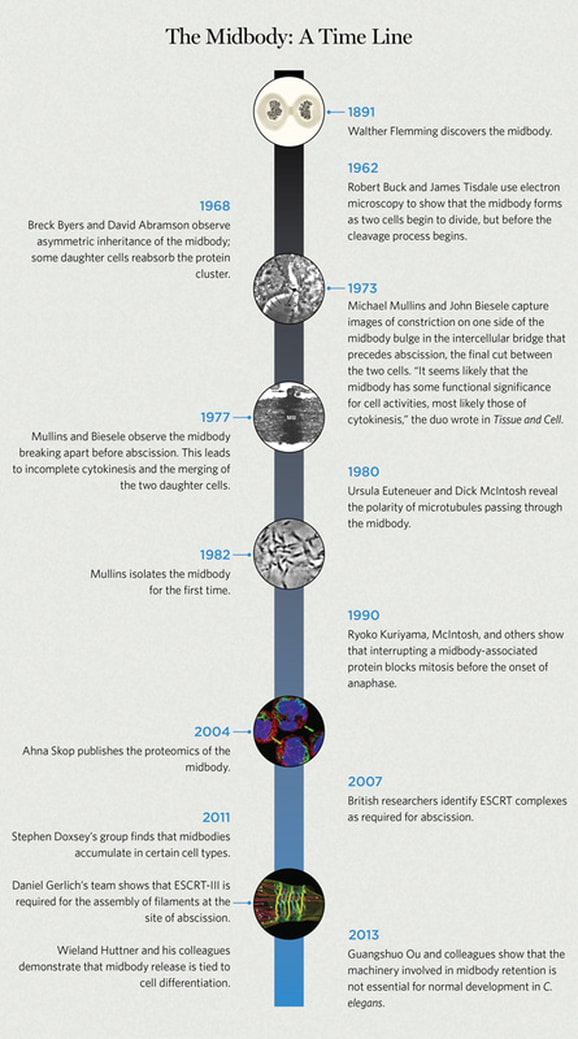
Everything you wanted to know about the midbody and were afraid to ask
Everything you wanted to know about the midbody and were afraid to ask